MM002-LS 21Wxx AT Commands
!!! UNDER CONSTRUCTION !!!
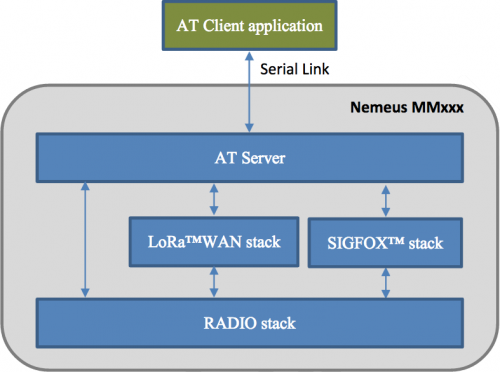
AT commands are used as an interface with Nemeus Communication modules. Modules can be driven at 3 different levels:
- Radio level: embedded AT server uses RF SX127x driver API (LoRa™and FSK modulations can be used).
- LoRa™WAN level: embedded AT server uses LoRa™WAN library API (available only when the library is present in embedded software).
- SIGFOX™ level: embedded AT server uses SIGFOX™ library API (available only when the library is present in embedded software).
When radio level is used, no device personalization is required, it is up to AT client application to implement network layer according to the network the device is attached (the module doesn’t know the network).
When LoRa™WAN level is used, the device is personalized with the following parameters:
- Whatever the activation type, a 64 bits device unique identifier.
- When Activation By Personalization (ABP) is used:
- An AES128 network session key for MIC computation and encryption of MAC control commands on port 0.
- An AES128 application session key for encryption of application payloads (not required when data encryption is disabled on the module).
- A device address
- When Over The Air Activation (OTAA) is used:
- A 64 bits join server unique identifier.
- An AES128 Key used to derive the network and application session keys.
The modules are personalized with Nemeus OUI during production phase and they can’t be modified. The device unique identifier is read-only and the AES128 keys are hidden.
The application unique identifier is modifiable by AT command.
When SIGFOX™ level is used, the device is personalized with the following parameters:
- The read-only device unique identifier.
- The hidden AES128 security key.
- The initial read-only Portability Access Code (PAC).
Before driving the module, the AT client application must activate the level it wants to use.
LoRa™WAN and SIGFOX™ levels can be activated in parallel, it is called the dual mode.
Radio level can't be activated in parallel with LoRa™WAN and/or SIGFOX™ levels.
For evaluation/test purpose, Nemeus recommends to use NemeusATK java application to drive the module.
Contents
- 1 UART configuration
- 2 AT commands
- 3 Generic Parameter description
- 4 Generic Response description
- 5 AT Generic commands
- 6 AT RF commands
- 6.1 AT+RF=HELP
- 6.2 AT+RF=ON
- 6.3 AT+RF=OFF
- 6.4 AT+RF=?
- 6.5 AT+RF=RPER
- 6.6 AT+RF=SPER
- 6.7 AT+RF=RSW
- 6.8 AT+RF=SSW
- 6.9 AT+RFTX=HELP
- 6.10 AT+RFTX=?
- 6.11 AT+RFTX=SET
- 6.12 AT+RFTX=SEND, (for test purpose)
- 6.13 AT+RFTX=START (for test purpose)
- 6.14 AT+RFTX=STOP (for test purpose)
- 6.15 AT+RFTX=SNDTXT,
- 6.16 AT+RFTX=SNDBIN,
- 6.17 AT+RFRX=HELP
- 6.18 AT+RFRX=?
- 6.19 AT+RFRX=SET,
- 6.20 AT+RFRX=RECV (for test purpose)
- 6.21 AT+RFRX=START (for test purpose)
- 6.22 AT+RFRX=STOP
- 6.23 AT+RFRX=CONTRX
- 6.24 AT+RFRX=LVL (for test purpose)
- 6.25 Informative examples
- 7 AT LoRa™WAN (MAC) commands
- 7.1 AT+MAC=HELP
- 7.2 AT+MAC=ON,
- 7.3 AT+MAC=OFF
- 7.4 AT+MAC=?
- 7.5 AT+MAC=SNDBIN
- 7.6 AT+MAC=RCVBIN
- 7.7 AT+MAC=SNDTXT
- 7.8 AT+MAC=RCVTXT
- 7.9 AT+MAC= STOPRCV
- 7.10 AT+MAC=SNDLCR
- 7.11 AT+MAC=RCH
- 7.12 AT+MAC=SCH,
- 7.13 AT+MAC= RDR
- 7.14 AT+MAC=SDR,
- 7.15 AT+MAC=RTI
- 7.16 AT+MAC= STI,
- 7.17 AT+MAC=RRX
- 7.18 AT+MAC=SRX,
- 7.19 AT+MAC=RSW
- 7.20 AT+MAC=SSW,
- 7.21 AT+MAC=RVAR
- 7.22 AT+MAC=SVAR,
- 7.23 AT+MAC=RADR
- 7.24 AT+MAC=SADR,
- 7.25 AT+MAC=RDEVUID
- 7.26 AT+MAC=RDEVADDR
- 7.27 AT+MAC=SDEVADDR,
- 7.28 AT+MAC=RAPPUID
- 7.29 AT+MAC=SAPPUID,
- 7.30 AT+MAC=RAPPKEY
- 7.31 AT+MAC=RNSKEY
- 7.32 AT+MAC=RAPPSKEY
- 7.33 AT+MAC=RMC
- 7.34 AT+MAC=SMC
- 7.35 Informative examples
- 8 AT SIGFOX™ commands
- 9 AT Generic command
- 10 AT debug command
- 11 AT Static Context Header Compression (SCHC) command
1 UART configuration
The UART configuration for Modem connection is as follows:
- Baud Rate : 38400
- Data : 8 bits
- Parity : None
- Stop : 1 bit
- Flow control : None
- End line character : <LF>
E.g. Typical configuration given by ‘stty’ command on linux:
speed 38400 baud; rows 0; columns 0; line = 0;
intr = ^C; quit = ^\; erase = ^?; kill = ^U; eof = ^D; eol = <undef>; eol2 = <undef>;swtch = <undef>; start = ^Q; stop = ^S; susp = ^Z; rprnt = ^R; werase = ^W; lnext = ^V;flush = ^O; min = 1; time = 0;
-parenb -parodd cs8 hupcl -cstopb cread clocal –crtsct signbrk -brkint -ignpar -parmrk -inpck -istrip -inlcr -igncr -icrnl -ixon -ixoff –iuclc -ixany -imaxbel -iutf8
-opost -olcuc -ocrnl -onlcr -onocr -onlret -ofill -ofdel nl0 cr0 tab0 bs0 vt0 ff0 -isig -icanon -iexten -echo -echoe -echok -echonl -noflsh -xcase -tostop –echoprt -echoctl -echoke
2 AT commands
At command are split according to communication layers. This is a list of main AT commands for SW given in ‘compatibility’ paragraph. The full list and limitation can be found in SW delivery note.
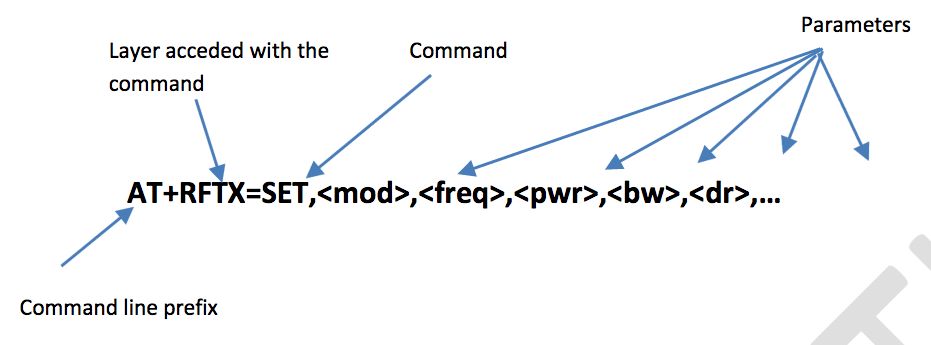
Formalism is the following:
For each group among RF, RFRX, RFTX, MAC and SFX, the command AT+<group>= HELP describes available sub-commands. Example:
AT+MAC= HELP +MAC: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +MAC: <cmd> are ON,OFF,?,SET,SCH,RCH,STI,RTI,SRX,RRX,SNDTXT,SNDBIN,RCVTXT,RCVBIN,STOPRCV,SNDLCR,DEVUID,DEVADDR,APPUID,APPKEY,NSKEY,APPSKEY +MAC: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
When a sub-command has parameter, AT+<group>= <cmd>? Describes the parameter list. Example:
AT+MAC=SNDTXT? +MAC: SNDTXT,<textpayload>,<nbrepeat>,<port>,<mode> OK
When command is unknown “command not found (‘try help’)” is returned.
AT commands are not cancelable, thus AT client application must wait for AT response before sending a new command.
Due to UART Rx buffer size, an AT command can't exceeds 511 characters.
3 Generic Parameter description
Following table describes mains parameters used with AT commands.
|
Values |
Description |
Type |
|
<mod> |
Modulation to be use |
LORA/FSK |
|
<freq> |
Carrier frequency |
Expressed in Hertz * |
|
<pwr> |
Tx power (range depends on Module definition; e.g. MM001 -1dBm to 14dBm) |
In dBm *
|
|
<bw> |
Bandwidth from 125kHz to 500 kHz |
In Hertz *
|
|
<dr> |
Spreading Factor in LoRa mode Data rate in FSK mode |
6/7 to 12 * In kb/s |
|
<cr> |
Coding Rate (LoRa mode only) |
1 to 4 |
|
<min/maxdr> |
Data rate range |
SF7BW125 to SF12BW125, SF7BW250 or FSK50KBPS |
|
<tx/rxcrcon> |
Flag for CRC check activation in TX or RX |
True or false |
|
<preamble> |
Length of the preamble |
6 to 65535 |
|
<f_dev> |
Frequency deviation (FSK mode only) |
|
|
<fixed_len> |
In RFTX commands: false means PHY header indicates the payload size, true means PHY payload is constant (no header) and equal to the sent payload length In RFRX commands: 0 means Rx payload length is decoded in PHY header, >0 means the Rx payload size is constant and equal to <fixed_len> value |
True or false (RFTX) Decimal value (RFRX) |
|
<tx/rxiqinv |
Flag for IQ inversion in TX or RX (LoRa mode only) |
True or false |
|
<rxw1> |
Delay before RX windows 1 |
In ms |
|
<rxw2> |
Delay before RX windows 2 ; NOTE: rx_w2 must be longer than rx_w1. |
In ms |
|
<tstamp> |
Rx ot Tx timestamp |
In ticks |
|
<symbtimeout> |
Number of symbols before RX timeout |
5 to 1023 |
|
<port> |
MAC port |
0 to 10 |
|
<textpayload> |
Payload to send or received payload in ASCII |
ASCII string |
|
< binarypayload> |
Payload to send or received payload in hexadecimal coded in ASCII |
ASCII string containing 0 to F characters |
|
<chan> |
Identifies one of the 8 MAC channels |
0 to 7 |
|
<enable> |
Indicates the status of a channel |
True or false |
|
<nbrepeat> |
Number of repetitions when sending a payload. At MAC level this parameter indicates if data confirmed must be used or not (0 means unacked mode>). |
0 to N |
|
<interval> |
Time interval between repetitions |
In ms |
|
<hexaddress> |
Address of a registry in hexadecimal |
|
|
<nbbytes> |
|
0 to 4 |
|
<byteN> |
Byte to write |
0x00 to 0xFF |
|
<margin> |
Link demodulation margin above the demodulation floor computed by the nearest gateway |
0 to 254 in dB |
|
<gwcnt> |
Number of gateways which received the MAC message |
1 to N |
|
<devuid> |
Device unique identifier |
8 bytes |
|
<devaddr> |
Device address (4 LSB of <devuid>) |
4 bytes |
|
<more> |
Indicates if more downlink data is pending |
true or false |
|
<mode> |
LoRa MAC transmission mode |
0 for confirmed data not 0 for unconfirmed data |
|
<rxw1freq> |
Channel frequency used for Rx window 1 |
In Hz, 0 means same as Tx frequency |
|
<eirp> |
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power received in TxParamSetupReq (Asian band only) |
In dBm |
|
<updwell> |
Uplink dwell time received in TxParamSetupReq (Asian band only) |
0 means no limit 1 means 400 ms |
|
<dwdwell> |
Downlink dwell time received in TxParamSetupReq (Asian band only) |
0 means no limit 1 means 400 ms |
|
<backoff> |
Ack mode retransmission back-off procedure |
false means disabled true means enabled |
- Depends on Module in use
4 Generic Response description
Every AT command send a response of one of the following types:
|
Values |
Description |
Visible output |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
<CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
OK response
|
OK |
|
<CR><LF>ERROR<CR><LF> |
ERROR response
|
ERROR |
|
<CR><LF>ERROR NOACK<CR><LF> |
ERROR response due to a missing ACK |
ERROR_NOACK
|
|
<CR><LF>+MAC: |
Response from MAC layer
|
+MAC: |
|
<CR><LF>+RFTX: |
Response from RF layer (TX)
|
+RFTX: |
|
<CR><LF>+RFRX: |
Response from RF layer (RX)
|
+RFRX: |
|
<CR><LF>+DEBUG: |
Response from debug layer |
+DEBUG: |
|
|
|
|
5 AT Generic commands
Intentionally left blank
6 AT RF commands
RF commands are dealing with the RF Layer. This layer should be started before using most of RF commands listed in this section (unless stated otherwise).
3 groups of commands exist:
- +RF group: commands common to TX and RX functions.
- +RFTX group: commands dedicated to TX functions.
- +RFRX group: commands dedicated to RX functions.
6.1 AT+RF=HELP
This command is used to know the list of sub-commands.
6.1.1 Response
OK.
6.1.2 Example
AT+RF=HELP +RF: <cmd> +RF: <cmd> are ON,OFF,?,RPER,SPER,RSW,SSW +RF: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
6.2 AT+RF=ON
This command is used to start RF layer (Radio driver) and is mandatory in order to use most of RF commands listed in this section (unless otherwise stated).
6.2.1 Response
ERROR is returned if either LoRa™WAN stack or SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio (Tx or Rx is ongoing).
Else OK is returned.
If LoRa™WAN stack was ON (but not using the radio), it is automatically set to OFF.
If SIGFOX™ stack was ON (but not using the radio), it is automatically set to OFF.
6.3 AT+RF=OFF
This command is used to stop RF layer (Radio driver). After calling this command, most of RF commands listed in this section will return ERROR (unless stated otherwise).
RF layer stop (Radio driver).
6.3.1 Response
Always OK.
6.4 AT+RF=?
This command is used to read the current RF layer state.
6.4.1 Response
Always OK.
6.4.2 Example
AT+RF=? +RF: OFF OK
6.5 AT+RF=RPER
This command is used to read the Packet Error Rate state, the power offset, the RSSI offset for LoRa/LoRaWAN carrier sensing, the RSSI offset for FSK/Sigfox carrier sensing and the frequency offset for Sigfox Tx.
6.5.1 Response
Always OK.
+RF: <per_state>,<pwroffset>,<loracsoffset>,<fskcsoffset>,<freqoffset>
6.5.2 Example
AT+RF=RPER +RF: false,0,12,-5,0 OK
6.6 AT+RF=SPER
This command is used to set the Packet Error Rate state, the power offset, the RSSI offset for LoRa/LoRaWAN carrier sensing, the RSSI offset for FSK/Sigfox carrier sensing and the frequency offset for Sigfox Tx.
The following formalism is used. It can be checked by the AT+RF=SPER?command:
+RF=SPER,<per_state>,<pwroffset>,<loracsoffset>,<fskcsoffset>,<freqoffset>
<per_state> PER state, unchanged when absent (string true or false).
<pwroffset> is the Power offset (signed decimal in dBm)
<loracsoffset> is the RSSI offset in LoRa (signed decimal in dB)
<fskcsoffset> is the RSSI offset in Fsk and Sigfox (signed decimal in dB)
<freqoffset> is the frequency offset in Sigfox (signed decimal in Hz)
When PER state is true, a counter is added at the beginning of Tx frames. This counter is used on Rx side to compute the Packet Error Rate.
6.6.1 Response
OK if <per_state> is “true”, “false” or omitted.
ERROR if <per_state> is syntactically incorrect.
6.6.2 Example
AT+RF=SPER,true OK
6.7 AT+RF=RSW
This command is used to read the current LoRa and FSK synchro words. Synchro words are in hexadecimal format (see formalism on SSW command)
6.7.1 Response
Always OK.
6.7.2 Example
AT+RF=RSW +RF: 12,69817E96 OK
6.8 AT+RF=SSW
This command is used to set the synchro words.
AT+RF=SSW,<LoRa_SyncWord>,<Fsk_SyncWord>
<LoRa_SyncWord> LoRa Synchro Word (one byte encoded as hexas digits)
<Fsk_SyncWord> FSK Synchro Word (up to six bytes encoded as hexa digits)
A synchro word is unchanged when related parameter is absent.
6.8.1 Response
OK if parameters are correct or omitted.
ERROR if FSK synchro word is too long (6 bytes/12 hexa digits max) or number of digits is not even.
6.8.2 Example
AT+RF=SSW, 12,69817E96 OK
6.9 AT+RFTX=HELP
This command is used to know the list of sub-commands.
6.9.1 Response
OK.
6.9.2 Example
AT+RFTX=HELP +RFTX: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +RFTX: <cmd> are ?,SET,SEND,SNDTXT,SNDBIN,START,STOP +RFTX: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
6.10 AT+RFTX=?
Read TX parameters. This command does not need the RF layer to be ON.
6.10.1 Response
Always OK.
+RFTX: <mod>,<freq>,<pwr>,<bw>,<dr>,<cr>,<txcrcon>,<preamble>,<fdev>,<fixed_len>,<txiqinv>,<rxw1>,<rxw2>,<tstamp>,<symbtimeout>,<rxiqinv>,<rxcrcon>,<rxaftertx>
6.10.2 Example
AT+RFTX=? +RFTX : LORA,868100000,14,125000,7,1,true,8,0,false,false,0,0,0,5,false,true,false OK
6.11 AT+RFTX=SET
Write Tx parameters. This command does not need the RF layer to be ON. Only modified parameters can be specified.
The following formalism is used. It can be checked by the AT+RFTX=SET? command:
+RFTX= SET,<mod>,<freq>,<pwr>,<bw>,<dr>,<cr>,<txcrcon>,<preamble>,<fdev>,<fixed_len>,<txiqinv>,<rxw1>,<rxw2>,<tstamp>,<symbtimeout>,<rxiqinv>,<rxcrcon>,<rxaftertx>
The parameters <symbtimeout>, <rxiqinv> and <rxcrcon> are used only when an Rx window is specified.
<tstamp> is the absolute clock time of the module. If the time is over, the frame is immediately transmitted. Usually this timestamp is a delay added to an Rx timestamp (feature not fully implemented)
When <fixed_len> is true then the fixed length value is the size of the sent payload and the Rx side must know this size.
6.11.1 Response
Always OK.
6.11.2 Example
To set the <pwr> to 12 and the <txcrcon> to false:
AT+RFTX=SET,,,12,,,,false OK
6.12 AT+RFTX=SEND, (for test purpose)
Transmit <nb_frames> numbered frames every <interval> ms.
AT+RFTX= SEND,<nb_frames>,<interval>
Default values : <nb_frames> = 1, <interval> = 500 (ms).
If <per_state> is true (see AT+RF=SPER command), transmitted frames contain a counter on 4 bytes followed by a 32 bytes fixed pattern.
This command is used as a generator for Packet Error Rate (PER) computing.
6.12.1 Response
OK if <nb_frames> have been successfully sent.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF or if one frame has not been successfully sent.
6.12.2 Example
AT+RFTX=SEND,3,500 OK
6.13 AT+RFTX=START (for test purpose)
FSK continuous transmission.
6.13.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF.
6.13.2 Example
AT+RFTX=START OK
6.14 AT+RFTX=STOP (for test purpose)
Stop FSK continuous transmission.
6.14.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF.
6.14.2 Example
AT+RFTX=STOP OK
6.15 AT+RFTX=SNDTXT,
Repeat <nbrepeat> text frames every 500 ms.
AT+RFTX= SNDTXT,<txt>,<nbrepeat>
Default values : <nbrepeat> = 1.
<txt> parameter is transmitted as received on serial link, the module doesn’t manage any character set.
If <per_state> is true (see AT+RF=SPER command), a 4 bytes counter is added at the beginning of the frame.
6.15.1 Response
OK if <nbrepeat> have been successfully sent.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF or if one frame has not been successfully sent.
6.15.2 Example
AT+RFTX=SNDTXT,HELLO WORLD,3 OK
6.16 AT+RFTX=SNDBIN,
Repeat <nbrepeat> binary frames every 500 ms.
AT+RFTX= SNDBIN,<bin>,<nbrepeat>
Default values : <nbrepeat > = 1
<bin> parameter is hexadecimal coded in ASCII (2 ASCII characters for 1 binary byte).
If <per_state> is true (see AT+RF=SPER command), a 4 bytes counter is added at the beginning of the frame.
6.16.1 Response
OK if <nbrepeat> have been successfully sent.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF or if one frame has not been successfully sent.
6.16.2 Example
To send 2 times the 3 bytes 1A 2B 3C:
AT+RFTX=SNDBIN,1A2B3C,2 OK
6.17 AT+RFRX=HELP
This commandis used to know the list of sub-commands.
6.17.1 Response
OK.
6.17.2 Example
AT+RFRX=HELP +RFRX: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +RFRX: <cmd> are ?,SET,RECV,START,STOP,CONTRX,LVL +RFRX: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
6.18 AT+RFRX=?
Read RX parameters.
6.18.1 Response
Always OK.
+RFRX: <mod>,<freq>,<bw>,<dr>,<cr>,<rxcrcon>,<fixed_len>,<rxiqinv>,<timeout>,<symbtimeout>,<lnaboost>
<timeout> and <symbtimeout> parameters are no more used by radio stack (they are still present for compatibility with previous module versions).
6.18.2 Example
AT+RFRX=? ,true OK
6.19 AT+RFRX=SET,
Set Rx parameters. Only modified parameter can be specified.
The following formalism is used. It can be check by the AT+RFRX=SET?
command:<mod>,<freq>,<bw>,<dr>,<cr>,<rxcrcon>,<fixed_len>,<rxiqinv>,<timeout>,<symbtimeout>,<lnaboost>
<timeout> and <symbtimeout> parameters are no more used by radio stack (they are still present for compatibility with previous module versions).
6.19.1 Response
Always OK
6.19.2 Example
To set <dr> parameter to 7:
AT+RFRX=SET,,,,7 OK
6.20 AT+RFRX=RECV (for test purpose)
Single frame reception with PER computation if <per_state> is true (see +RF=SPER command).
RF layer comes back to IDLE state after reception or after AT+RFRX=STOP command.
6.20.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON and not already receiving.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF or is already receiving.
+RFRX: <per>,<rssi>,<snr>,<crcerr>,<tstamp>,<binary payload>
Then, when a frame is received the unsolicited response below is sent:
If <per_state> is true (see +RF=SPER command):
+RFRX: 100%,-35.00,7.00,0,1521551302,12000000CAFEDECA…
Where 100% is the PER, -35.00 is the RSSI level, 7.00 is the SNR, 0 is “no CRC error”, 1521551302 is the Rx clock time in ms and 12000000CAFEDECA is the received payload, starting with the 4 bytes counter.
If <per_state> is false:
+RFRX: ,-35.00,7.00,0,1521551302,CAFEDECA…
PER is not displayed and the 4 bytes counter is not present in the payload (it means that Tx device also has <per_state> set to false.
After frame reception the Rx is automatically stopped.
6.20.2 Example
AT+RFRX=RECV OK +RFRX: 100%,-35.00,7.00,0,1521551302,12000000CAFEDECA
6.21 AT+RFRX=START (for test purpose)
Continuous reception with PER computation if <per_state> is true (see +RF=SPER command).
RF layer stays in RX until Rx stop command is sent (see AT+RFRX=STOP)
6.21.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON and not already receiving. ERROR if RF layer is OFF or is already receiving.
When a TX has been performed during Reception, An AT+RFRX=STOP command may be needed to avoid ERROR from this command
After frame reception RF layer stays in RX (RX stop command must be used to leave RX mode).
6.21.2 Example
AT+RFRX=START OK +RFRX: 100%,-35.00,7.00,0,1521551302,12000000CAFEDECA +RFRX: 100%,-32.00,7.00,0,1521554506,13000000CAFEDECA …
6.22 AT+RFRX=STOP
Stop single or continuous reception.
6.22.1 Response
OK if RF layer is in RX.
ERROR if RF layer is not in RX.
6.22.2 Example
AT+RFRX=STOP OK
6.23 AT+RFRX=CONTRX
Continuous reception without PER computation.
6.23.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON and not already receiving.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF or is already receiving.
Then, for each received frame, the unsolicited response below is sent:
+RFRX: <rssi>,<snr>,<crcerr>,<tstamp>,<binary payload>
6.24 AT+RFRX=LVL (for test purpose)
Last reception parameters read (RSSI, SNR)
6.24.1 Response
OK if RF layer is ON.
ERROR if RF layer is OFF.
Response information is as below:
+RFRX: LVL,<rssi>,<snr>
6.24.2 Example
AT+RFRX=LVL +RFRX: LVL,-77.00,8.00 OK
6.25 Informative examples
6.25.1 LoRa Communication
Below is an example where two Modules are configured to communicate on a specific frequency.
First we setup the Module A and start a continuous RX, then we can setup the Module B.
Module A
AT+RF=ON OK |
|
AT+RFRX=SET,LORA,,125000,7 OK |
|
AT+RFRX=CONTRX OK |
|
….. |
|
+RFRX: -78.00,3.00,0,152987007,CAFE |
|
AT+RFRX=STOP |
|
Module B
AT+RF=ON OK |
|
AT+RFTX=SET,LORA,868100000,14,125000,7 OK |
|
AT+RFTX=SNDBIN,CAFE,1 OK |
|
….. |
|
6.25.2 FSK Communication
Below is an example where two Modules are configured to communicate on a specific frequency. For FSK some rules apply on selected "bandwith/datarate" in RX and "frequency deviation/datarate" in TX. This is described in (sx1272 datasheet)
First we setup the Module A and start a continuous RX, then we can setup the Module B.
Module A
AT+RF=ON OK |
|
AT+RFRX=SET,FSK,868100000,125000,1200 OK |
|
AT+RFRX=CONTRX OK |
|
….. |
|
+RFRX: -78.00,3.00,0,152987007,CAFE |
|
AT+RFRX=STOP |
|
Module B
AT+RF=ON OK |
|
AT+RFTX=SET,FSK,868100000,14,,1200,,,,50000 OK |
|
AT+RFTX=SNDBIN,CAFE,1 OK |
|
….. |
|
7 AT LoRa™WAN (MAC) commands
3 types of AT strings are specified:
- MAC commands: AT+MAC=<cmd>,<param1>,…,<paramN>.
- MAC solicited responses: +MAC: <param1>,…,<paramN>. These responses are sent in response to MAC commands, just before the OK response, that’s the reason why the <cmd> is not present in the solicited responses. Several solicited responses may be sent between the MAC command and the OK response.
- MAC unsolicited responses: +MAC: <cmd>,<param1>,…,<paramN>. These responses are not necessarily sent between the MAC command and the OK response, that’s the reason why the <cmd> is present in the unsolicited responses.
When an AT client application just need to send and receive frames, the following commands are used:
- AT+MAC=? to know the current MAC mode (OFF/ON, ABP/OTAA, Class A/C).
- AT+MAC=OFF and AT+MAC=ON,… to change the MAC mode.
- AT+MAC=DEVADRR and unsolicited +MAC: DEVADDR,… to know the current state of an OTAA device.
- AT+MAC=SNDBIN,… to send uplink frame.
- +MAC: RCVBIN,… when receiving downlink frames and to know Rx windows termination.
- +MAC: END to know when the LoRaWAN layer is back to idle.
All other commands are not really required, they are mainly used by NemeusATK Java application to manage the LoRa™WAN layer (for IOT purpose, device provisioning …).
7.1 AT+MAC=HELP
This commandis used to know the list of sub-commands.
7.1.1 Response
OK.
7.1.2 Example
AT+MAC= HELP +MAC: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +MAC: <cmd> are ON,OFF,?,SCH,RCH,SDR,RDR,STI,RTI,SRX2,RRX2,SNDTXT,SNDBIN,RCVTXT,RCVBIN,STOPRCV,SNDLCR,DEVUID,DEVADDR,APPUID,APPKEY,NSKEY,APPSKEY +MAC: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
7.2 AT+MAC=ON,
This command is used to start LoRa™WAN layer and is mandatory in order to use most of MAC commands listed in this section (unless otherwise stated).
If Radio stack was ON, it is automatically set to OFF.
AT+MAC=ON,<minor_ver>,<class>,<otaa>
- <minor_ver> is deprecated, only the default value (3) is accepted
- <class> is A or C.
- <otaa> is 0 for ABP and 1 for OTAA.
7.2.1 Response
If SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio ERROR is returned.
Else OK is returned.
7.2.2 Example
Start LoRa™WAN layer in class A with OTAA:
AT+MAC=ON,,A,1 OK
7.3 AT+MAC=OFF
Stop LoRa™WAN layer.
7.3.1 Response
Always OK.
7.4 AT+MAC=?
Read current LoRa™WAN layer status.
To change LoRa™WAN layer status, AT+MAC=OFF and AT+MAC=ON,… must be performed.
7.4.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <state>,<minor_ver>,<class>,<ch_pages>,<ism_band>,<otaa>
<state> is ON, OFF or DUAL. DUAL means that LoRa™WAN and SIGFOX™ stacks are both ON.
<minor_ver> always V3.
<class> is A or C.
<page> is the number of pages of 16 channels available at LoRa™WAN layer (in terms of memory space), 1 page for EU863-870, AS923 and RU864-870, 5 pages for US902-928..
<ism_band> is 8 for EU863-870MHz, 9 for US902-928MHz, 10 for AS923MHz and 13 for RU864-870MHz. ISM band can’t be modified dynamically, it is set at compilation time.
<otaa> is 0 for ABP and 1 for OTAA.
7.4.2 Example
A class A US902-928MHz device with 80 channels (5*16) in OTAA:
AT+MAC=? +MAC: ON,V3,A,5,9,1 OK
7.5 AT+MAC=SNDBIN
Binary frame transmission.
AT+MAC= SNDBIN,<binpayload>,<nbrepeat>,<port>,<mode>,<add_tx_rx_info>,<dev_time_req>
If <mode> value is 0 then the frame is sent in unacknowledged mode (default value when mode is omitted).
If <mode> value is > 0, then the frame is sent in acknowledged mode.
<nbrepeat> specifies the number of repetitions in acknowledged mode (0 when omitted). Since LoRaWANV1.0.4 the <nbtrans> parameter is also used in acknowledged mode (see RDR/SDR commands), thus if (<nbrepeat>+1) <= <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent <nbtrans> times, if (<nbrepeat>+1) > <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent 2*<nbtrans> times, ...
If <port> is omitted then port 2 is used by default (port 1 is reserved to embedded generic application).
if <add_tx_rx_info> > 0 then for each transmission performed and each Rx performed the following responses are sent after the +RCVBIN:
+MAC: TXINFO,<tx_index>,<tx_freq>,<toa>
+MAC: RXINFO,<rx_index>,<rx_freq>,<toa>
if <dev_time_req> > 0 then a device time request is added in the MAC header of the uplink frame
7.5.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and frame has been successfully sent (and acked if acked mode was requested).
ERROR if MAC is OFF or frame has not been successfully sent (or not acked after repetitions if acked mode was requested).
ERROR also if SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio.
ERROR also when port is reserved regarding LoRa™WAN standard.
7.5.2 Unsolicited responses
The unsolicited responses below are sent when AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: SND,<busytime>
<busytime> is in ms.
This unsolicited response can be sent 2 times:
- One time with busytime > 0 if no channel was free due to duty cycle restriction
- One time with busytime = 0 at Tx time.
+MAC: RCH,<chan>,,,,,<busytime>,<page>
<busytime> is in ms.
Sent for each enabled channel.
+MAC: END
To indicate when LoRaWAN layer is back to idle.
7.5.3 Example
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,1A2B3C,3,2,0
+MAC: SND,4355
+MAC: SND,0
+MAC: RCH,0,,,,,4480,0
+MAC: RCH,1,,,,,4480,0
+MAC: RCH,2,,,,,4480,0
OK
+MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,,0.00,0.00
+MAC: END
On duty cycle expiry (4480 ms after the Tx), channels become available:
+MAC: RCH,0,,,,,0,0
+MAC: RCH,1,,,,,0,0
+MAC: RCH,2,,,,,0,0
7.6 AT+MAC=RCVBIN
Register for receiving downlink frames on specified port, payload is output as binary hexa string.
AT+MAC= RCVBIN,<port>
This command is no more required because all downlink frames are routed on serial link except when the port is used by an embedded application.
7.6.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and port is valid and free.
ERROR if MAC is OFF or port is invalid or port is already used by an embedded application.
7.6.2 Unsolicited Response
+MAC: RCVBIN,<port>,<more>,<binarypayload>,<rssi>,<snr>
When <more> is true, it means that more downlink frames are pending in MAC server. If piggyback setting is disabled and device class is A, LoRa™WAN layer will automatically poll the server to receive more downlink frames.
The RCVBIN unsolicited response is always sent after a Tx, even if no frame has been received. It indicates the end of Rx windows.
For a class A device, it is sent when a downlink frame has been received or at the end of the Rx window 2 (if no downlink frame has been received).
For a class C device, it is sent when a downlink frame has been received or at the end of the Rx window 1 (if no downlink frame has been received).
If the Tx was in ack mode, the RCVBIN is sent before the OK (or ERROR NOACK) response of the Tx (SNDBIN or SNDTXT command).
If the Tx was in unack mode, the RCVBIN is sent after the OK response of the Tx (SNDBIN or SNDTXT command).
7.6.3 Example
AT+MAC= RCVBIN,2 OK
Then when a frame is received on port 2 and more downlink frames are pending:
+MAC: RCVBIN,2,true,1A2B3C4D,-43.00,7.00
7.7 AT+MAC=SNDTXT
It is the same command as AT+MAC=SNDBIN except that the payload is interpreted as text and is transmitted as received on serial link (no translation from hexa ASCII to hexa binary is performed).
AT+MAC= SNDTXT,<textpayload>,<nbrepeat>,<port>,<mode>,<add_tx_rx_info>,<dev_time_req>
Text frame transmission.
If <mode> value is 0 then the frame is sent in unacknowledged mode (default value when mode is omitted).
If <mode> value is > 0, then the frame is sent in acknowledged mode.
<nbrepeat> specifies the number of repetitions in acknowledged mode (0 when omitted). Since LoRaWANV1.0.4 the <nbtrans> parameter is also used in acknowledged mode (see RDR/SDR commands), thus if (<nbrepeat>+1) <= <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent <nbtrans> times, if (<nbrepeat>+1) > <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent 2*<nbtrans> times, ...
If <port> is omitted then port 2 is used by default (port 1 is reserved to embedded generic application).
if <add_tx_rx_info> > 0 then for each transmission performed and each Rx performed the following responses are sent after the +RCVBIN:
+MAC: TXINFO,<tx_index>,<tx_freq>,<toa>
+MAC: RXINFO,<rx_index>,<rx_freq>,<toa>
if <dev_time_req> > 0 then a device time request is added in the MAC header of the uplink frame
7.7.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and frame has been successfully sent (and acked if acked mode was requested).
ERROR if MAC is OFF or frame has not been successfully sent (or not acked after repetitions if acked mode was requested).
ERROR also if SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio.
ERROR also when port is reserved regarding LoRa™WAN standard.
7.7.2 Unsolicited responses
The unsolicited responses below are sent when AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: SND,<busytime>
<busytime> is in ms.
This unsolicited response can be sent 2 times:
- One time with busytime > 0 if no channel was free due to duty cycle restriction
- One time with busytime = 0 at Tx time.
+MAC: RCH,<chan>,,,,,<busytime>,<page>
<busytime> is in ms.
Sent for each enabled channel.
7.7.3 Example
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,HELLO WORLD,3,2,0
+MAC: SND,4355
+MAC: SND,0
+MAC: RCH,0,,,,,4480,0
+MAC: RCH,1,,,,,4480,0
+MAC: RCH,2,,,,,4480,0
OK
+MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,,0.00,0.00
+MAC: END
On duty cycle expiry (4480 ms after the Tx), channels become available:
+MAC: RCH,0,,,,,0,0
+MAC: RCH,1,,,,,0,0
+MAC: RCH,2,,,,,0,0
7.8 AT+MAC=RCVTXT
Register for receiving downlink frames on specified port, payload is output as text string (translation to binary hexa string is not performed).
AT+MAC=RCVTXT,<port>
This command is no more required because all downlink frames are routed on serial link except when the port is used by an embedded application.
By default, downlink payload are processed as binary payload, thus if the AT client application needs to receive the payload as text (without any binary hexa string translation), it must uses this command.
7.8.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and port is valid and free.
ERROR if MAC is OFF or port is invalid or port is already used by an embedded application.
7.8.2 Unsolicited Response
+MAC: RCVTXT,<port>,<more>,<textpayload>,<rssi>,<snr>
When <more> is true, it means that more downlink frames are pending in MAC server. If piggyback setting is disabled and device class is A, LoRa™WAN layer will automatically poll the server to receive more downlink frames.
7.8.3 Example
AT+MAC=RCVTXT,2 OK
Then when a frame is received on port 2 and more downlink frames are pending:
+MAC: RCVTXT,2,true,HELLO WORLD,-43.00,7.00
7.9 AT+MAC= STOPRCV
Unregister for receiving downlink frames on specified port.
AT+MAC=STOPRCV,<port>
7.9.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and port is valid.
ERROR if MAC is OFF or port is invalid.
7.10 AT+MAC=SNDLCR
Send a Link Check Request.
AT+MAC=SNDLCR,<nb_tx><add_tx_rx_info>
<nb_tx> = 0 means the LCR message is sent in unack mode on port 0.
<nb_tx> != 0 means the LCR message is sent in ack mode on port 0. Since LoRaWANV1.0.4 the <nbtrans> parameter is also used in acknowledged mode (see RDR/SDR commands), thus if <nb_tx> <= <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent <nbtrans> times, if <nb_tx> > <nbtrans> then the frame will be sent 2*<nbtrans> times, ...
if <add_tx_rx_info> > 0 then for each transmission performed and each Rx performed the following responses are sent after the +MAC: <margin>,...
+MAC: TXINFO,<tx_index>,<tx_freq>,<toa>
+MAC: RXINFO,<rx_index>,<rx_freq>,<toa>
7.10.1 Response
OK if MAC is ON and Link Check Answer has been received.
ERROR if MAC is OFF or Link Check Answer has not been received and Tx was in unack mode.
ERROR NOACK if Link Check Answer has not been received and Tx was in ack mode.
ERROR also if SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio.
Received data is sent back as
+MAC: <margin>,<gwcnt>,<rssi>,<snr>
7.10.2 Example
AT+MAC=SNDLCR +MAC: 20,3,-45.00,8.00 OK
7.11 AT+MAC=RCH
Read MAC channels command.
AT+MAC=RCH,<chan>,<page>,<unsol_evt>
<chan> specifies the channel to read (all channels of the page if omitted or if 16)
<page> specifies the channel page (all pages if omitted or if number of available pages returned by AT+MAC=? response).
<unsol_evt> specifies which unsolicited events are required (0 when no event required). The unsolicited events inform the AT client application when a MAC parameter has been changed by the LoRa™WAN layer.
When <unsol_evt> length is less than 4 digits then the old meaning is decoded (0: no event, >0: all events except the transaction end event)
When <unsol_evt> length is coded on 4 hexa digits then it is a decoded as a bit field:
bit0: registration to +SND: <busytime> event
bit1: registration to +RCH: <chan_idx>,,,,,<busytime>,<page> event
bit2: registration to +SCH: <chan>,<frequency>,<mindr>,<maxdr>,<dutycycle>,<busytime>,<page>,<rxw1freq> event
bit3: registration to +RDR: <dr>,<txpwr>,<chanmask>,<chanmaskctrl>,<nbtrans>,<eirp>,<updwell>,<dwdwell>,<antennagain> event (<eirp>, <updwell>, <dwdwell> and <antennagain> parameters are present only in case of Asian band firmware)
bit4: registration to +RTI: <rxw1>,<rxw2>,<symbtimeout> event
bit5: registration to +RRX: <rx2frequency>,<rx2dr>,<rx1droffset> event
bit6: registration to +RVAR: <delay> event
bit7: registration to +SND: <delay> event
7.11.1 Response
OK if parameters are syntactically correct.
For each channel, the following information is output:
+MAC: <chan>,<frequency>,<mindr>,<maxdr>,<dutycycle>,<busytime>,<page>,<rxw1freq>
<chan>: the channel index in the page (0 to 15).
<frequency>: the frequency in Hz (0 means channel is disabled).
<mindr>: minimum datarate allowed on the channel.
<maxdr>: maximum datarate allowed on the channel.
<dutycycle>: restricted duty cycle assigned to the channel (applies only when more restricted than ISM regulation specification).
<busytime>: time in ms before the channel can be used again for Tx (due to duty cycle restrictions).
<page>: channel page (0 to number of available pages returned by AT+MAC=? response).
<rxw1freq>: frequency used to open Rx window 1. 0 means same frequency as <frequency> parameter (available only from LoRaWAN V1.0.2, if the parameter is absent in the response, it means the firmware version is older).
7.11.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when <busytime> changes and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: RCH,<chan>,,,,,<busytime>,<page>
7.11.3 Example
AT+MAC=RCH +MAC: 0,868100000,SF12BW125,SF7BW125,100,0,0,0 +MAC: 1,868300000,SF12BW125,SF7BW125,100,0,0,869525000 +MAC: 2,868500000,SF12BW125,SF7BW125,100,0,0,0 +MAC: 3,868850000,SF12BW125,SF7BW125,1000,0,0,0 … +MAC: 15,000000000,SF12BW125,FSK50KBPS,1,0,0,0 OK
7.12 AT+MAC=SCH,
Set MAC channel command.
AT+MAC=SCH,<chan>,<frequency>,<min_dr>,<max_dr>,<dutycycle>,<page>
Only modified parameters can be specified.
Written parameters are not saved in file system, thus they are lost after a new MAC OFF/ON or a device reset.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SCH?Command.
<dutycycle> is applied only if it is more restricted than the ISM regulation specification. 1 means 100%, 10 means 10%, 100 means 1%, ...
<rxw1freq> is available only from LoRaWAN V1.0.2
7.12.1 Response
OK if parameters are syntactically correct.
7.12.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when LoRa™WAN layer modifies a channel and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: SCH,<chan>,<frequency>,<mindr>,<maxdr>,<dutycycle>,<page>,<rxw1freq>
7.12.3 Example
To modify channel 0:
AT+MAC=SCH,0,868100000,SF12BW125,SF7BW125,100,0,0 OK
7.13 AT+MAC= RDR
Read current MAC datarate command.
7.13.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <dr>,<txpwr>,<chanmask>,<chanmaskctrl>,<nbtrans>,<eirp>,<updwell>,<dwdwell>,<antennagain>
<eirp>, <updwell>, <dwdwell> and <antennagain> parameters are present only in case of Asian band firmware
7.13.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when current datarate changes and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: RDR,<dr>,<txpwr>,<chanmask>,<chanmaskctrl>,<nbtrans>,<eirp>,<updwell>,<dwdwell>,<antennagain>
7.13.3 Example
AT+MAC=RDR +MAC: SF12BW125,11,001F,0,0 OK
7.14 AT+MAC=SDR,
Set MAC data rate command.
AT+MAC=SDR,<dr>,<txpwr>,<chanmask>,<chanmaskctrl>,<nbtrans>,<eirp>,<updwell>,<dwdwell>,<antennagain>
Only modified parameters can be specified.
Written parameters are not saved in file system, thus they are lost after a new MAC OFF/ON or a device reset.
Set the data rate, Tx power and number of transmissions for uplink transmission (applied to all channels compatible with the datarate). <nbtrans> applies to unconfirmed and confirmed transmissions.
<chanmask> and <chanmaskctrl> specify the channels usable for uplink access.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SDR?Command.
<eirp>, <updwell>, <dwdwell> and <antennagain> parameters are present only in case of Asian band.
Programmed Tx power = <eirp> - 2*TxPower - <antennagain> (TxPower is described in LoRaWANRegionalParameters specification: 0=>MaxEIRP, 1=>MaxEIRP-2dB, ...)
Because of SX1272 hardware, Tx power = 13 dBm is never programmed, 14 dBm is set instead.
Thus when <eirp> = 16 and <antennagain> = 3 then computed Tx power = 13 dBm but programmed Tx power = 14 dBm
The maximum Tx power supported by the standard version of MM002 is 14 dBm, so when (<eirp> - <antennagain>) > 14 dBm then 14 dBm is programmed
7.14.1 Response
OK if parameters are syntactically correct.
7.14.2 Example
To modify current datarate:
AT+MAC=SDR,SF12BW125,10,001F,0,0
OK
7.15 AT+MAC=RTI
Read MAC Time Information command.
Read common channel time information.
7.15.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <rxw1>,<rxw2>,<symbtimeout>
7.15.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when current time info changes and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: RTI,<rxw1>,<rxw2>,<symbtimeout>
7.15.3 Example
AT+MAC= RTI +MAC: 1000,2000,6 OK
7.16 AT+MAC= STI,
Set MAC time information command.
AT+MAC=STI,<rxw1>,<rxw2>,<symbtimeout>
Only modified parameter can be specified.
Written parameters are not saved in file system, thus they are lost after a new MAC OFF/ON or a device reset.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=STI?Command.
The parameters <rxw1> and <symbtimeout> are common to all channels.
The <rxw2> parameter is no more used because <rxw2> value is set to <rxw1> value + 1000 ms. It is still present for compatibility with old devices.
7.16.1 Response
Always OK.
7.16.2 Example
To modify time info:
AT+MAC=STI,1000,,6 OK
7.17 AT+MAC=RRX
Read MAC Rx information command.
7.17.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <rx2frequency>,<rx2dr>,<rx1droffset>
7.17.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when current Rx info changes and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: RRX,<rx2frequency>,<rx2dr>,<rx1droffset>
7.17.3 Example
AT+MAC=RRX +MAC: 869525000,SF9BW125,0 OK
7.18 AT+MAC=SRX,
Set MAC Rx information command.
Only modified parameters can be specified.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SRX?Command.
The parameters are common to all channels.
7.18.1 Response
OK if parameters are syntactically correct.
7.18.2 Example
To modify Rx parameters:
AT+MAC=SRX,869525000,SF9BW125,0 OK
7.19 AT+MAC=RSW
This command is used to read the current LoRa™ and FSK synchro words used by LoRa™WAN layer. Synchro words are in hexadecimal format.
7.19.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <LoRa™ sync_word>,<FSK sync_word>
7.19.2 Example
AT+MAC=RSW +MAC: 34,C194C1 OK
7.20 AT+MAC=SSW,
This command is used to set the synchro words used by LoRa™WAN layer.
AT+MAC=SSW,<LoRaSyncWord>,<FskSyncWord>
Only modified parameters can be specified.
A synchro word is unchanged when related parameter is absent.
Synchro words are in hexadecimal.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SSW?Command.
7.20.1 Response
OK if parameters are correct or omitted.
ERROR if FSK synchro word is too long (6 bytes/12 hexa digits max) or number of digits is not even.
7.20.2 Example
AT+MAC=SSW,34,C194C1 OK
7.21 AT+MAC=RVAR
This command is used to read the miscellaneous LoRa™WAN variables.
This variables are Tx/Rx counters, aggregated DC and data encryption.
7.21.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <txcounter>,<rxcounter>,<aggregateddc>,<encryption>
<aggregateddc> values: 1 means 100%, 10 means 10%, 100 means 1%, …
<encryption> values: 0 means no encryption, != 0 means encryption enabled.
7.21.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent only when current aggregated DC changes and AT client application has registered to receive unsolicited events (see AT+MAC=RCH command).
+MAC: RVAR,,,<aggregateddc>
7.21.3 Example
AT+MAC=RVAR +MAC: 0,0,1,1 OK
7.22 AT+MAC=SVAR,
This command is used to set some LoRa™WAN variables.
AT+MAC=SVAR,<txcounter>,<aggregateddc>,<encryption>
Only modified parameters can be specified.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SVAR?Command.
7.22.1 Response
Always OK.
7.22.2 Example
To disable encryption:
AT+MAC=SVAR,,,0 OK
7.23 AT+MAC=RADR
This command is used to read the current LoRa™WAN ADR, piggyback and back-off states.
The ack mode retransmission back-off procedure was initially linked to ADR bit. When ADR bit was on/off, the back-off procedure was on/off. From now, the back-off procedure is linked to the back-off state, it allows to enable ADR bit without enabling the back-off procedure. If <backoff> parameter is absent in RADR response, it means that back-off procedure is still linked to ADR bit (older firmware version).
7.23.1 Response
Always OK.
+MAC: <adr>,<piggyback>,<backoff>
<adr>, <piggyback> and <backoff> values: true or false.
7.23.2 Example
AT+MAC=RADR +MAC: true,false,false OK
7.24 AT+MAC=SADR,
This command is used to set some LoRa™WAN ADR and piggyback states.
AT+MAC=SADR,<adr>,<piggyback>,<backoff>
Only modified parameters can be specified.
The parameter list can be found by AT+MAC=SADR?Command.
When ADR state value is changed, ADR ack counter is reset.
7.24.1 Response
OK if parameters are correct.
7.24.2 Example
To enable piggyback:
AT+MAC=SADR,,true OK
7.25 AT+MAC=RDEVUID
Read device unique identifier.
Device UID is coded on 8 bytes.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=DEVUID command.
Old command still works and returns the same response.
7.25.1 Response
Always OK
UID is returned as
+MAC: <devuid>,<rand_seed>,<read_only>
When read_only value is 1, it means that the device unique identifier is built from Nemeus 36 bits OUI (70B3D5326xxxxxxx). In this case the device UID can’t be modified and the security keys are not readable.
7.25.2 Example
AT+MAC=RDEVUID 0010203,306A0327,1 OK
7.26 AT+MAC=RDEVADDR
Read device address.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=DEVADDR command.
Old command still works and returns the same solicited response.
Warning: unsolicited response changed, old one is no more sent!!!
7.26.1 Response
Always OK
Address is returned as
+MAC: <devaddr>,<networkid>
In ABP mode, the device address is the 4 LSB of the device unique identifier.
In OTAA mode, the device address is assigned by the network.
7.26.2 Unsolicited response
The unsolicited response below is sent when device is in OTAA mode and at least one AT+MAC=? command has been sent.
+MAC: RDEVADDR,<devaddr>,<networkid>
7.26.3 Example
Read device address of an OTAA device when not yet joint to network:
AT+MAC=? +MAC: ON,V3,A,1,8,1 OK AT+MAC=RDEVADDR +MAC: 00000000,000000 OK
After receipt of valid join accept, unsolicited response is sent:
DEVADDR,0870C367,010203
7.27 AT+MAC=SDEVADDR,
This command is used to modify device address when ABP mode is used.
AT+MAC=SDEVADDR,<devaddr>
If MAC layer is on in ABP mode, a MAC off/on is automatically performed.
7.27.1 Response
OK if <devaddr> length is 8 characters.
7.27.2 Example
AT+MAC=SDEVADDR,01020304 OK
7.28 AT+MAC=RAPPUID
Read application Unique ID.
Application UID is coded on 8 bytes.
By default it is set to 0000000000000000.
It can be modified by sending the following AT command:
AT+GA=DIND,1,8301000008xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx0000
Where xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx is the new application UID LSB first.
MAC layer must be restarted to take into account new application UID (AT+MAC=OFF and AT+MAC=ON).
Application UID can also be modified using AT+MAC=SAPPUID,<app_uid>.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=APPUID command.
Old command still works and returns the same response.
7.28.1 Response
Always OK
Application UID is returned as
+MAC: <appuid>
7.28.2 Example
Read default application UID:
AT+MAC=RAPPUID +MAC: 0000000000000000 OK
Set application UID to FEDCBA9876543210:
0000 OK
Restart MAC layer:
AT+MAC=OFF OK AT+MAC=ON OK
Read new application UID:
AT+MAC=RAPPUID +MAC: FEDCBA9876543210 OK
7.29 AT+MAC=SAPPUID,
This command is used to modify application UID.
AT+MAC=SAPPUID,<appuid>
If MAC layer is on in OTAA mode, a MAC off/on is automatically performed.
7.29.1 Response
OK if <appuid> length is 16 characters.
7.29.2 Example
AT+MAC=SAPPUID,0102030405060708 OK
7.30 AT+MAC=RAPPKEY
Read application key.
Application Key is coded on 16 bytes.
The byte order is the one you can use when you to register the key at network side.
It has been reversed compared to old AT+MAC=APPKEY response.
This command is available only when device unique identifier is not read only.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=APPKEY command.
Old command still works and returns the <appkey> in reverse order.
7.30.1 Response
OK when device UID is writable.
ERROR when device UID is read only.
Application key is returned as
+MAC: <appkey>
7.30.2 Example
AT+MAC=RAPPKEY +MAC: A8FA642E2E3245BB9B8CAC7E2456EF3C OK
Old command still returns:
AT+MAC=APPKEY +MAC: 3CEF56247EAC8C9BBB45322E2E64FAA8 OK
7.31 AT+MAC=RNSKEY
Read Network Session Key.
Network Session Key is coded on 16 bytes.
The byte order is the one you can use when you to register the key at network side.
It has been reversed compared to old AT+MAC=NSKEY response.
This command is available only when device unique identifier is not read only.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=NSKEY command.
Old command still works and returns the <nskey> in reverse order.
7.31.1 Response
OK when device UID is writable.
ERROR when device UID is read only.
Network session key is returned as
+MAC: <nskey>
7.31.2 Example
AT+MAC=RNSKEY +MAC: A8F1642E2E32453B9B8CAC7C2456EF72 OK
Old command still returns:
AT+MAC=NSKEY +MAC: 72EF56247CAC8C9B3B45322E2E64F1A8 OK
7.32 AT+MAC=RAPPSKEY
Read application session key.
Application session key is coded on 16 bytes.
The byte order is the one you can use when you to register the key at network side.
It has been reversed compared to old AT+MAC=APPSKEY response.
This command is available only when device unique identifier is not read only.
This command obsoletes AT+MAC=APPSKEY command.
Old command still works and returns the <appskey> in reverse order.
7.32.1 Response
OK when device UID is writable.
ERROR when device UID is read only.
Application session key is returned as
+MAC: <appskey>
7.32.2 Example
AT+MAC=RAPPSKEY +MAC: A8FA672E2E4245BB9ECCCA7E64F54C38 OK
Old command still returns:
AT+MAC=APPSKEY +MAC: 384CF5647ECACC9EBB45422E2E67FAA8 OK
7.33 AT+MAC=RMC
Read MultiCast parameters. Multicast is only available from master18Wxx.
7.33.1 Response
OK when the command is supported by the firmware.
ERROR when it is not supported.
Multicast parameters are returned as
+MAC: <addr>,<addr_mask>,<group_mask>,<fcnt_dw>,<net_skey>,<app_skey>
- <addr>: the multicast address (32 bits) - <addr_mask>: the significant part of the multicast address (More Significant bits) coded on 32 bits. - <group_mask>: the groups the device can receive (32 bits => groups 0 to 31). - <fcnt_dw>: the current value of the downlink frame counter (32 bits). - <net_skey>: the network security key for integrity checking (128 bits). - <app_skey>: the application security key for payload ciphering (128 bits).
The address mask specifies which part of the received address is processed as an address and which part is processed as a group. The address mask can take the following values:
- 0x00000000: the multicast function is disabled - 0xFFFFFFFF: only 1 group is possible - 0xFFFFFFFE: 2 groups are possible - 0xFFFFFFFC: 4 groups are possible - 0xFFFFFFF8: 8 groups are possible - 0xFFFFFFF0: 16 groups are possible - 0xFFFFFFE0: 32 groups are possible
7.33.2 Example
AT+MAC=RMC +MAC: 789ABCDE,FFFFFFFC,00000007,0,0102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F00,0102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F00 OK
With such parameters, the following received addresses are processed:
- 0x789ABCDC: valid multicast address, group 0 is accepted because bit0 of group mask is set - 0x789ABCDD: valid multicast address, group 1 is accepted because bit1 of group mask is set - 0x789ABCDE: valid multicast address, group 2 is accepted because bit2 of group mask is set - 0x789ABCDF: valid multicast address, group 3 is rejected because bit3 of group mask is not set
When the address is accepted (valid multicast address and accepted group) then the MIC is computed thanks to network security key. If the computed MIC matches with the received MIC then the payload is deciphered thanks to application security key and the resulting payload is pushed to the application addressed by the LoRaWAN port.
7.34 AT+MAC=SMC
Set MultiCast parameters. Multicast is only available from master18Wxx.
AT+MAC=SMC,<addr>,<addr_mask>,<group_mask>,<fcnt_dw>,<net_skey>,<app_skey>
See AT+MAC=RMC for parameter description.
The multicast parameters are not saved in non volatile memory, thus they are lost after a cold reset (reset pin or power-cycle).
7.34.1 Response
OK when the command is supported by the firmware and the parameters are valid.
ERROR when it is not supported or parameters are invalid (especially <group_mask> parameter which can take 7 different values).
7.34.2 Example
AT+MAC=SMC,789ABCDE,FFFFFFFC,00000007,0,0102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F00,0102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F00 OK
7.35 Informative examples
7.35.1 Device start
AT client application can detect a device start or restart when the unsolicited response +DEBUG: START,<version> is received. Depending on initialization timing, AT client application is not sure to receive this unsolicited response, that’s the reason why it is recommended that AT client application use AT+MAC=? command to synchronize with the device.
OTAA case:
+DEBUG: START,Nemeus-mm002-MASTER_NEMEUS_15W39-data-manager AT+MAC=? +MAC: ON,V3,A,1,8,1 OK AT+MAC=RDEVADDR +MAC: 00000000,000000 OK +MAC: RDEVADDR,0870C367,010203
The device is ready to send uplink frames.
ABP case:
+DEBUG: START,Nemeus-mm002-MASTER_NEMEUS_15W39-data-manager AT+MAC=? +MAC: ON,V3,A,1,8,0 OK
The device is ready to send uplink frames.
7.35.2 Send unconfirmed binary frame
No downlink frame:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,0 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,,0.00,0.00
One downlink frame:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,0 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DECA,-85.00,7.00
Two downlink frames and piggyback is not set:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,0 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,true,DECA,-55.00,10.00 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DEFC,-73.00,9.00
Two downlink frames and piggyback is set:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,0 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,true,DECA,-55.00,10.00 AT+MAC=SNDBIN,,0,2,0 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DEFC,-73.00,9.00
7.35.3 Send confirmed binary frame
Ack received, no downlink frame:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,0,false,,-60.00,7.00 OK
Ack not received:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,,0.00,0.00 ERROR NOACK
One downlink frame:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DECA,-85.00,7.00 OK
Two downlink frames and piggyback is not set:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,true,DECA,-55.00,10.00 OK +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DEFC,-73.00,9.00
Two downlink frames and piggyback is set:
AT+MAC=SNDBIN,CAFE,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,true,DECA,-55.00,10.00 OK AT+MAC=SNDBIN,,0,2,1 +MAC: RCVBIN,2,false,DEFC,-73.00,9.00 OK
8 AT SIGFOX™ commands
These commands are available only on Nemeus modules embedding SIGFOX™ library. If the library is not embedded then ERROR is returned.
3 type of AT strings are specified:
- SF commands: AT+SF=<cmd>,<param1>,…,<paramN>.
- SF solicited responses: +SF: <param1>,…,<paramN>. These responses are sent in response to SF commands, just before the OK response, that’s the reason why the <cmd> is not present in the solicited responses. Several solicited responses may be sent between the SF command and the OK response.
- SF unsolicited responses: +SF: <cmd>,<param1>,…,<paramN>. These responses are not necessarily sent between the SF command and the OK response, that’s the reason why the <cmd> is present in the unsolicited responses.
When an AT client application just need to send and receive frames, the following commands are used:
- AT+SF=? to know the current SIGFOX™ layer state.
- AT+SF=OFF and AT+SF=ON to stop and start SIGFOX™ layer.
- AT+SF=SNDBIN,… to send uplink frame.
- AT+SF=SNDBIT,… to send uplink bit.
- AT+SF=SNDOOB to send uplink out of band message (keep alive messages).
- +SF: RCVBIN,… when receiving downlink frames.
All other commands are not really required, they are mainly used to configure SIGFOX™ layer and to perform SIGFOX™ qualification tests.
SIGFOX™ proprietary AT command set is also supported but not described in this document.
8.1 AT+SF=HELP
This commandis used to know the list of sub-commands.
8.1.1 Response
OK.
8.1.2 Example
AT+SF=HELP +SF: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +SF: <cmd> are ON,OFF,?,SNDBIN,SNDBIT,SNDOOB,SREP,RREP,STXF,RTXF,SRXF,RRXF,STXP,RTXP +SF: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
8.2 AT+SF=ON
This command is used to start SIGFOX™ layer and is mandatory in order to use most of SF commands listed in this section (unless otherwise stated).
If Radio stack was ON, it is automatically set to OFF.
8.2.1 Response
If LoRa™WAN stack is using the radio ERROR is returned.
Else OK is returned.
8.2.2 Example
AT+SF=ON OK
8.3 AT+SF=OFF
Stop SIGFOX™ layer.
8.3.1 Response
If SIGFOX™ stack is using the radio ERROR is returned.
Else OK is returned.
8.3.2 Example
AT+SF=OFF OK
8.4 AT+SF=?
Read current SIGFOX™ layer status.
8.4.1 Response
If SIGFOX™ library is embedded OK is returned.
Else ERROR is returned.
+SF: <state>,<NMS_lib_ver>,<SFX_lib_ver>,<dev_id>,<initial_pac>
<state> is ON, OFF or DUAL. DUAL means that LoRa™WAN and SIGFOX™ stacks are both ON.
<NMS_lib_ver> is the version of Nemeus library used to communicate with SIGFOX™ network.
<SFX_lib_ver> is the version of SIGFOX™ library.
<dev_id> is the device unique identifier on SIGFOX™ network.
<initial_pac> is the first Portability Access Code used to register the device on SIGFOX™ network. It is used one time for first registration.
8.4.2 Example
AT+SF=? +SF: ON,NMS-SFX-LIB-1.2,UDL1-1.6.0,000ABCDE,0123456789ABCDEF OK
8.5 AT+SF=SNDBIN,
Binary frame transmission.
AT+SF=SNDBIN,<binpayload>,<ack>
If <ack> value is 0 then the frame is sent in unacknowledged mode (default value when <ack> is omitted).
If <ack> value is 1, then the frame is sent in acknowledged mode.
The frame is sent when channel becomes free regarding duty cycle limitations.
8.5.1 Response
+SF: <time_on_air> is sent just before the solicited response OK. The time on air is in ms, it is used by client application to manage duty cycle.
OK if SIGFOX™ layer is ON and frame has been successfully sent (and acked if ack mode was requested).
ERROR if SIGFOX™ layer is OFF or frame has not been successfully sent (or not acked after repetitions if ack mode was requested).
8.5.2 Unsolicited responses
An indication about Tx date:
+SF: SND,<busytime>
<busytime> is in ms.
It can be sent 2 times:
- One time with busytime > 0 if Tx subband was not free due to duty cycle restriction
- One time with busytime = 0 at Tx time.
The unsolicited response below is sent when ack mode was requested.
+SF: RCVBIN,<binpayload>,<rssi>
8.5.3 Example
AT+SF=SNDBIN,CAFE,1 +SF: SND,4576 +SF: SND,0 +SF: 6282 OK +SF: RCVBIN,0123456789ABCDEF,-85.00
8.6 AT+SF=SNDBIT,
Bit transmission.
AT+SF=SNDBIT,<bitvalue>,<ack>
If <ack> value is 0 then the bit is sent in unacknowledged mode (default value when <ack> is omitted).
If <ack> value is 1, then the bit is sent in acknowledged mode.
8.6.1 Response
+SF: <time_on_air> is sent just before the solicited response OK. The time on air is in ms, it is used by client application to manage duty cycle.
OK if SIGFOX™ layer is ON and frame has been successfully sent (and acked if ack mode was requested).
ERROR if SIGFOX™ layer is OFF or frame has not been successfully sent (or not acked after repetitions if ack mode was requested).
8.6.2 Unsolicited responses
An indication about Tx date:
+SF: SND,<busytime>
<busytime> is in ms.
It can be sent 2 times:
- One time with busytime > 0 if Tx subband was not free due to duty cycle restriction
- One time with busytime = 0 at Tx time.
The unsolicited response below is sent when ack mode was requested.
+SF: RCVBIN,<binpayload>,<rssi>
8.6.3 Example
AT+SF=SNDBIT,0,1 +SF: SND,6422 +SF: SND,0 +SF: 4589 OK +SF: RCVBIN,0123456789ABCDEF,-85.00
8.7 AT+SF=SNDOOB
Out Of Band message transmission.
8.7.1 Response
+SF: <time_on_air> is sent just before the solicited response OK. The time on air is in ms, it can be used by client application to manage duty cycle.
OK if SIGFOX™ layer is ON and frame has been successfully sent.
ERROR if SIGFOX™ layer is OFF or frame has not been successfully sent.
8.7.2 Unsolicited responses
An indication about Tx date:
+SF: SND,<busytime>
<busytime> is in ms.
It can be sent 2 times:
- One time with busytime > 0 if Tx subband was not free due to duty cycle restriction
- One time with busytime = 0 at Tx time.
8.7.3 Example
AT+SF=SNDOOB +SF: SND,3987 +SF: SND,0 +SF: 4589 OK
8.8 AT+SF=RREP
Read Tx repetitions used in acked mode.
8.8.1 Response
+SF: <repeat> is sent just before the solicited response OK.
Default value is 2 repetitions.
Always OK.
8.8.2 Example
AT+SF=RREP +SF: 2 OK
8.9 AT+SF=SREP,
Set Tx repetitions used in acked mode.
AT+SF=SREP,<repeatnb>
8.9.1 Response
Default value is 2 repetitions.
OK if number of repetitions <= 2.
ERROR if number of repetitions > 2.
8.9.2 Example
AT+SF=SREP,1 OK AT+SF=SREP,3 ERROR
8.10 AT+SF=RTXF
Read output carrier macro channel.
8.10.1 Response
+SF: <tx_frequency> is sent just before the solicited response OK.
Default value is 868130000 Hz.
Always OK.
8.10.2 Example
AT+SF=RTXF +SF: 868130000 OK
8.11 AT+SF=STXF,
Set output carrier macro channel.
8.11.1 Response
OK if 863000000 <= tx_frequency <= 870000000.
ERROR if tx_frequency is not in valid range.
8.11.2 Example
AT+SF=STXF,868200000 OK AT+SF=STXF,862200000 ERROR
8.12 AT+SF=RRXF
Read reception carrier macro channel.
8.12.1 Response
+SF: <rx_frequency> is sent just before the solicited response OK.
Default value is 869525000 Hz.
Always OK.
8.12.2 Example
AT+SF=RRXF +SF: 869525000 OK
8.13 AT+SF=SRXF,
Set reception carrier macro channel.
AT+SF=SRXF,<rx_frequency>
8.13.1 Response
OK if 863000000 <= rx_frequency <= 870000000.
ERROR if rx_frequency is not in valid range.
8.13.2 Example
AT+SF=SRXF,869525000 OK AT+SF=SRXF,869525000 ERROR
8.14 AT+SF=RTXP (for test purpose)
Read Tx power applied to FSK continuous wave
8.14.1 Response
+SF: <tx_power> is sent just before the solicited response OK.
Default value is 14 dBm.
Always OK.
8.14.2 Example
AT+SF=RTXP +SF: 14 OK
8.15 AT+SF=STXP (for test purpose)
Set Tx power applied to FSK continuous wave
8.15.1 Response
OK if tx_power <= 14 dBm.
ERROR if tx_power > 14 dBm.
8.15.2 Example
AT+SF=STXP,10 OK AT+SF=STXP,20 ERROR
9 AT Generic command
AT Generic command can be used to activate/deactivate some generic functionalities.
9.1 AT+GA= DIND,1,8801
This command is use to know the status of PowerSaving.
9.1.1 Response
+GA : DIND,1,0801<pwr_state>
Always OK.
pwr_state 00 powersaving OFF pwr_state 01 powersaving ON
9.1.2 Example
AT+GA= DIND,1,8801
+GA : DIND,1,080100
OK.
9.2 AT+GA= DIND,1,8802<pwr_state>
WARNING: CONNECT CORRECTLY THE WAKEUP PIN BEFORE ACTIVATION OF POWERSAVING
This command is use to set the PowerSaving.
pwr_state 00 powersaving OFF
pwr_state 01 powersaving ON
PowerSaving can be activated once after boot-up, and from this point will go in stop mode as soon as possible and is wake-up by RTC or Wakeup pin. Please note that once power-saving is activated, user should toggle wake-up pin before sending an AT command.
If the module is reset, the powersaving is set back to OFF. So User should ensure setting it to ON after any reset
9.2.1 Response
Always OK.
9.2.2 Example
AT+GA= DIND,1,880201
OK
10 AT debug command
AT debug command can be used to activate/deactivate some debug functionalities.
10.1 AT+DEBUG= HELP
This commandis use to know the list of sub-commands.
10.1.1 Response
OK.
10.1.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= HELP +DEBUG: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +DEBUG: <cmd> are MVER,MVOFF,MVON,MV?,MEOFF,MEON,ME?,MPOFF,MPON,MP?,RREAD,RWRITE +DEBUG: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
10.2 AT+DEBUG=MVER
Read Mcu software version.
Furthermore, when the device boots the software version is sent as an unsolicited response:
+DEBUG: START,<version>
This unsolicited response can be used to detect a reset of the device.
10.2.1 Response
Always OK.
+DEBUG: MVER,<version>
10.2.2 Example
AT boot:
+DEBUG: START,Nemeus 1.x
When requested:
AT+DEBUG= MVER +DEBUG: MVER,Nemeus 1.x OK
10.3 AT+DEBUG= MVOFF
Disable Mcu Verbose print on the UART
10.3.1 Response
Always OK.
10.3.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MVOFF OK
10.4 AT+DEBUG= MVON
Enable Mcu Verbose print on the UART
10.4.1 Response
OK if software is compiled with debug traces.
ERROR if software is compiled without debug traces.
10.4.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MVON OK
10.5 AT+DEBUG= MV?
Read current verbose mode.
10.5.1 Response
Always OK.
+DEBUG: <verbose>
10.5.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MV? +DEBUG: MVON OK
10.6 AT+DEBUG= MEOFF
Disable UART echo mode.
10.6.1 Response
Always OK.
10.6.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MEOFF OK
10.7 AT+DEBUG= MEON
Enable UART echo mode.
10.7.1 Response
Always OK.
10.7.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MEON OK
10.8 AT+DEBUG= ME?
Read current echo mode.
10.8.1 Response
Always OK.
+DEBUG: <echo>
10.8.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= ME? +DEBUG: MEON OK
10.9 AT+DEBUG= MPOFF
Disable the sending of shell prompt on UART.
10.9.1 Response
Always OK.
10.9.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MPOFF OK
10.10 AT+DEBUG= MPON
Enable the sending of shell prompt on UART.
10.10.1 Response
Always OK.
10.10.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MPON OK
10.11 AT+DEBUG= MP?
Read current prompt mode.
10.11.1 Response
Always OK.
+DEBUG: <prompt>
10.11.2 Example
AT+DEBUG= MP? +DEBUG: MPON OK
11 AT Static Context Header Compression (SCHC) command
AT SCHC command can be used to communicate through Acklio IPCore network.
Currently, the default firmware doesn't support SCHC command.
11.1 AT+SCHC=HELP
This command is used to know the list of sub-commands.
11.1.1 Response
OK.
11.1.2 Example
AT+SCHC=HELP +SCHC: <cmd>,<param_1>,…,<param_N> +SCHC: <cmd> are VER,RL2,SL2,RSTATE,SSTATE,SOCKET,RSOCKET,CLOSE,BIND,SENDTO +SCHC: <cmd>? Lists parameters of <cmd> if any OK
11.2 AT+SCHC=VER
Read version of SCHC stack.
11.2.1 Response
Always OK.
+SCHC: <version>
<version>: the library version
11.2.2 Example
AT+SCHC=VER +SCHC: 2.0.0 OK
11.3 AT+SCHC=RL2
Read available L2 which can be used by SCHC stack.
11.3.1 Response
Always OK.
For each LoRaWAN L2:
+SCHC: <l2_id>,<l2_type>,<join_chan_mask>,<join_dr>,<first_dr>,<adr>,<nb_trans>,<piggyback>,<backoff>,<force_dr>,<ack>,<class_c>
<l2_id>: the identifier which addresses the L2 <l2_type>: 0 for LoRaWAN <join_chan_mask>: channels used by join procedure 0 for ABP mode, 1 for 868.1 channel, 2 for 868.3 channel, 4 for 868.5 channel, 7 for all default channels <join_dr>: data rate to start the join procedure (0 to 5) <first_dr>: data rate of the first uplink frame sent after the join procedure <adr>: ADR bit (0 or 1) <nb_trans>: number of transmissions of unconfirmed frames (0 to 15) <piggyback>: piggyback enable(1)/disable(0) <backoff>: backoff when confirmed frames are unacked enable(1)/disable(0) <force_dr>: forced data rate (15 means do not force, use current one) <ack>: ack mode enable(1)/disable(0) <class_c>: device class C enable(1)/disable(0)
For Sigfox L2:
Not yet available
11.3.2 Example
AT+SCHC=RL2 +SCHC: 0,0,7,0,15,1,0,0,0,15,0,1 OK
11.4 AT+SCHC=SL2
Set L2 parameters.
For a LoRaWAN L2:
AT+SCHC=SL2,<l2_id>,<join_chan_mask>,<join_dr>,<first_dr>,<adr>,<nb_trans>,<piggyback>,<backoff>,<force_dr>,<ack>,<class_c>
For Sigfox L2:
Not yet available
11.4.1 Response
OK when all specified parameters are valid.
11.4.2 Example
AT+SCHC=SL2,0,7,0,15,1,0,0,0,15,0,1 OK
11.5 AT+SCHC=RSTATE
Read current state of SCHC stack.
11.5.1 Response
Always OK.
Response to command:
+SCHC: <r_state>,<l2_id>
<r_state>: the current SCHC stack state: 0 when stack is off, 1 when stack is initializing (joining when LoRaWAN L2), 2 when stack is idle, 3 when stack is transmitting <l2_id>: the L2 used by SCHC stack
Unsolicited response (when stack state changes):
+SCHC: RSTATE,<r_state>,<l2_id>
11.5.2 Example
AT+SCHC=RSTATE +SCHC: 0,0 OK
11.6 AT+SCHC=SSTATE
Set state of SCHC stack. AT+SCHC=SSTATE,<s_state>,<l2_id>
<s_state>: the requested SCHC stack state: 0 to switch-off the stack, 1 to initialize the stack <l2_id>: the L2 the SCHC stack must use
11.6.1 Response
OK when all specified parameters are valid.
Unsolicited response (when stack state changes):
+SCHC: RSTATE,<r_state>,<l2_id>
11.6.2 Example
Switch-on the stack with l2_id 0
AT+SCHC=SSTATE,1,0 OK +SCHC: RSTATE,1,0 +SCHC: RSTATE,2,0
Switch-off the stack
AT+SCHC=SSTATE,0 OK +SCHC: RSTATE,0,0
11.7 AT+SCHC=SOCKET
Create a socket.
AT+SCHC=SOCKET,<ip_version>,<compression>
<ip_version>: 4 for IPv4, 6 for IPv6 <compression>: NONE for no compression, LIGHT for light compression, FULL for full compression
11.7.1 Response
OK when all specified parameters are valid, maximum number of sockets (1) is not reached and SCHC stack is on.
Response to command:
+SCHC: <sock_id>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier
11.7.2 Example
AT+SCHC=SOCKET,6,FULL +SCHC: 0 OK
11.8 AT+SCHC=RSOCKET
List all created sockets.
AT+SCHC=RSOCKET
11.8.1 Response
Always OK.
Response to command:
For each socket:
+SCHC: <sock_id>,<ip_addr>,<port>,<compression>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier <ip_addr>: the bound IP address (32 characters for IPv6 and 8 characters for IPv4) <compression>: NONE, LIGHT or FULL
11.8.2 Example
AT+SCHC=RSOCKET +SCHC: 0,01020304,CDDC,LIGHT OK
11.9 AT+SCHC=BIND
Bind a socket on local IP address and port. AT+SCHC=BIND,<sock_id>,<ip_addr>,<port>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier <ip_addr>: the IP address to bind (32 characters for IPv6 and 8 characters for IPv4) <port>: the port to bind
11.9.1 Response
OK when all specified parameters are valid and the addressed socket exists
11.9.2 Example
AT+SCHC=BIND,0,01020304,CDDC OK
11.10 AT+SCHC=CLOSE
Close a socket. AT+SCHC=CLOSE,<sock_id>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier
11.10.1 Response
OK when the addressed socket exists
11.10.2 Example
AT+SCHC=CLOSE,0 OK
11.11 AT+SCHC=SENDTO
Send a frame on a socket. AT+SCHC=SENDTO,<sock_id>,<dest_ip_addr>,<dest_port>,<payload>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier <dest_ip_addr>: destination IP address (32 or 8 characters) <dest_port>: destination port (4 characters) <payload>: the payload to send (hexa string)
11.11.1 Response
OK when the addressed socket exists, there is no ongoing transmission and the transmission succeeded
Unsolicited response (when downlink payload is received):
+SCHC: RCVFROM,<sock_id>,<src_ip_addr>,<src_port>,<payload>
<sock_id>: the socket identifier <src_ip_addr>: source IP address (32 or 8 characters) <src_port>: source port (4 characters) <payload>: the received payload (hexa string)
11.11.2 Example
AT+SCHC=SENDTO,0,01020304,FDDF,CAFEDECA +SCHC: RSTATE,3,0 +SCHC: RSTATE,2,0 OK +SCHC: RCVFROM,0,01020304,FDDF,CAFECAFE