NIS-TR Temperature Sensor (RTD)
Contents
1 General information
2 Mechanics
- Dimensions 60 x 95 x 85mm (109mm including fixing brackets)
- 96mm spacing between brackets
- IP 65
- Solid ABS & PC material
3 RTD Temperature sensor properties
- Handles 100Ω to 1kΩ (at 0°C) Platinum RTDs (PT100 to PT1000)
- 2-wires, 3-wire or 4-wire connection
- 15-Bit ADC Resolution; Nominal Temperature Resolution 0.03125°C (Varies Due to RTD Nonlinearity)
- Total Accuracy Over All Operating Conditions: 0.5°C (0.05% of Full Scale) max
- ±45V Input Protection
- Fault Detection (Open RTD Element, RTD Shorted to Out-of-Range Voltage, or Short Across RTD Element)
- Direct fifth-order linearization for best accuracy
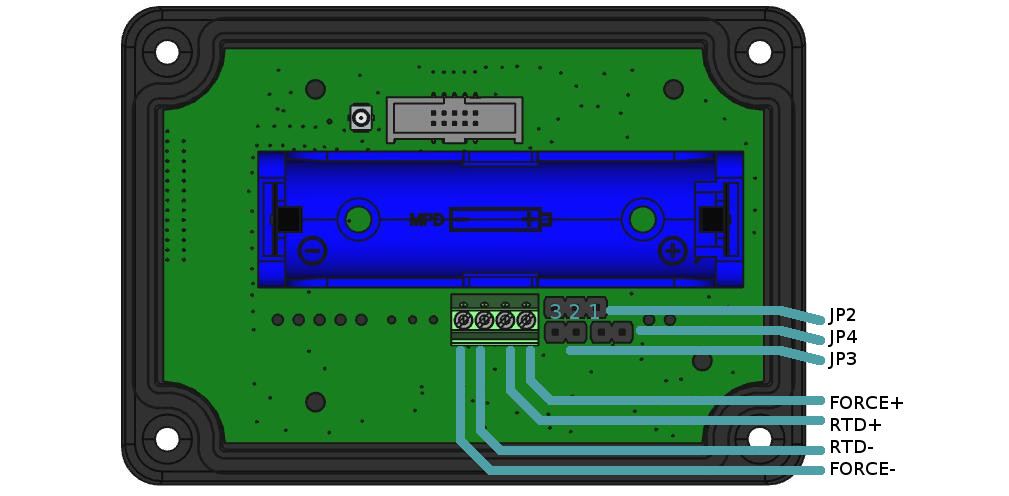
4 Wiring
| number of wires | jumpers configuration | Probe connection |
| 4 wires | JP2 jumper on 1-2 | FORCE+ IN+ IN- FORCE- |
| JP3 NC | ||
| JP4 NC | ||
| 3 wires | JP2 jumper on 2-3 | FORCE+ IN+ IN- |
| JP3 NC | ||
| JP4 jumper ON | ||
| 2 wires | JP2 jumper on 1-2 | IN+ IN- |
| JP3 jumper ON | ||
| JP4 jumper ON |
5 Magnetic Switch Protocol description
MSxxx Generic Magnetic Switch Protocol
6 Radio frames description
MSxxx Generic Application Protocol
6.1 Uplink data Frame format
The uplink payload contains multiple fields: <mask>: bit field on 1 byte indicating the presence of other fields. Bit 7 is always to 1 because the mask is never extended on next byte.
bit 0 : indicates the presence of <nb_meas> field.
bit 1 : indicates the presence of <rtd_temp> field.
bit 2 : indicates the presence of <voltage> field.
bit 3 : indicates the presence of <internal_temp> field.
bit 4 : is reserved.
bit 5 : indicates the presence of <cause> field.
When bit 0 is not set, it means that other fields are present only once (nb_meas = 1).
if (mask.bit0 == 1) :
<nb_meas>: 1 byte containing the number of measures which follow.
if (mask.bit1 == 1) :
<rtd_temp>: 2*<nb_meas> bytes containing the measured temperatures in 1/100 °C. Each temperature is a signed integer on 16 bits in big endian.
if (mask.bit2 == 1) :
<voltage>: 2*<nb_meas> bytes containing the voltages measured by the sensor in millivolts. Each voltage is an unsigned integer on 16 bits in big endian.
if (mask.bit3 == 1)
<internal_temp>: 1*<nb_meas> bytes containing the measured internal temperatures (using MCU internal sensor). Each temperature is a signed integer on 8 bits in big endian.
if (mask.bit5 == 1) :
<cause>: 1 byte containing the cause of the uplink frame. It is a bit field:
Bit 0 indicates a periodic measure
Bit 1 indicates the high threshold exceeding (temperature > high threshold)
Bit 2 indicates the high hysteresis exceeding (temperature < high threshold - high hysteresis)
Bit 3 indicates the low threshold exceeding (temperature < low threshold)
Bit 4 indicates the low hysteresis exceeding (temperature > low threshold + low hysteresis)
Bit 5 indicates the measure has been forced manually (with magnetic switch)
Usually <cause> field is absent when threshold detections are disabled (periodic measures only)
Thus the uplink frame format is <mask><nb_meas><rtd_temp1>...<rtd_tempN><voltage1>...<voltageN><internal_temp1>...<internal_tempN><cause>
Default <mask> value is 0x83 which means that the default frame is <mask><nb_meas><rtd_temp1>...<rtd_tempN>
Some examples (in hexadecimal):
“820AFA”: the frame indicates one temperature of +28.10 °C. “8302FDE80078”: the frame indicates two temperatures of -5.36 °c and +1.20 °C.
6.2 Downlink Frame format
The sensor configuration contains the following fields:
It is possible to change the sensor configuration using the Nemeus downlink protocol. The downlink frame must be sent on the MS008 ??? LoRaWAN port (8).
The downlink frame has the following format:
<cmd>: 1 byte containing WRITE_CFG_CMD=0x02
Some examples in hexadecimal: ...
6.3 Power consumption
Please find below a tool to calculate power consumption vs number of measures and transmissions.